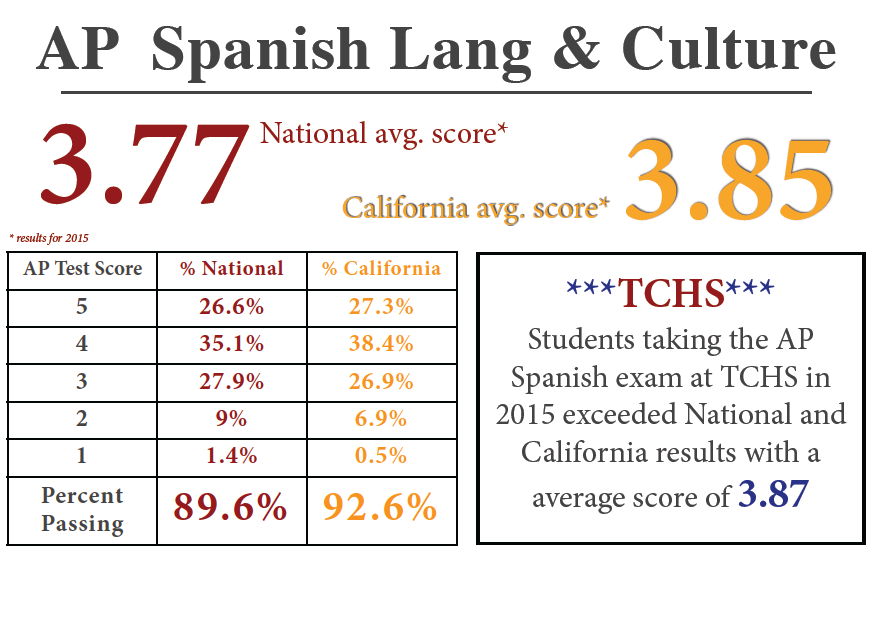
About AP Spanish Language
|
Course Themes:
The AP Spanish Language and Culture course is structured around six themes: • Beauty and Aesthetics • Contemporary Life • Families and Communities • Global Challenges • Personal and Public Identities • Science and Technology Themes facilitate the integration of language, content, and culture and promote the use of the language in a variety of contexts. |
How AP exams Are Scored
AP Exam Readers are thoroughly trained, and their work is monitored throughout the Reading for fairness
and consistency. In each subject, a highly respected college faculty member fills the role of Chief Reader,
who, with the help of AP Readers in leadership positions, maintains the accuracy of the scoring standards.
Scores on the free-response questions are weighted and combined with the results of the computer-scored
multiple-choice questions, and this raw score is converted into a composite AP score of 5, 4, 3, 2, or 1.
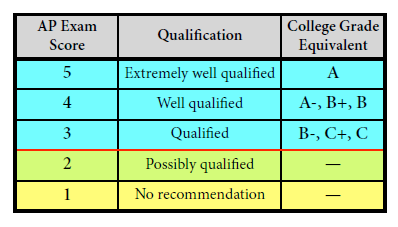
In general, an AP Exam score of 5 is equivalent to the average score among college students earning grades of A in the college course. Similarly, AP Exam scores of 4 are equivalent to college grades of A−, B+, and B.
AP Exam scores of 3 are equivalent to college grades of B−, C+, and C.
and consistency. In each subject, a highly respected college faculty member fills the role of Chief Reader,
who, with the help of AP Readers in leadership positions, maintains the accuracy of the scoring standards.
Scores on the free-response questions are weighted and combined with the results of the computer-scored
multiple-choice questions, and this raw score is converted into a composite AP score of 5, 4, 3, 2, or 1.
In general, an AP Exam score of 5 is equivalent to the average score among college students earning grades of A in the college course. Similarly, AP Exam scores of 4 are equivalent to college grades of A−, B+, and B.
AP Exam scores of 3 are equivalent to college grades of B−, C+, and C.
Using and interpreting AP ScoresThe extensive work done by college faculty and AP
teachers in the development of the course and the exam and throughout the scoring process ensures that AP Exam scores accurately represent students’ achievement in the equivalent college course. While colleges and universities are responsible for setting their own credit and placement policies, AP scores signify how qualified students are to receive college credit or placement. |