About AP Psychology
The AP Psychology course is designed to introduce students to the systematic and scientific study of the behavior and mental processes of human beings and other animals. Students are exposed to the psychological facts, principles, and phenomena associated with each of the major subfields within psychology. They also learn about the ethics and methods psychologists use in their science and practice.
The following is a list of learning objectives for the major
content areas covered in the AP Psychology Exam: 1. History and Approaches 2. Research Methods 3. Biological Bases of Behavior 4. Sensation and Perception 5. States of Consciousness 6. Learning 7. Cognition 8. Motivation and Emotion 9. Developmental Psychology 10. Personality 11. Testing and Individual Differences 12. Abnormal Behavior 13. Treatment of Abnormal Behavior 14. Social Psychology |
College Course equivalentThe Advanced Placement Program offers a course and exam in psychology to qualified students who wish to complete studies in secondary school equivalent to an introductory college course in psychology.
College Course equivalentThe Advanced Placement Program offers a
course and exam in psychology to qualified students who wish to complete studies in secondary school equivalent to an introductory college course in psychology. PrerequisitesThere are no prerequisites for the AP
Psychology course. |
How AP exams Are Scored
AP Exam Readers are thoroughly trained, and their work is monitored throughout the Reading for fairness
and consistency. In each subject, a highly respected college faculty member fills the role of Chief Reader,
who, with the help of AP Readers in leadership positions, maintains the accuracy of the scoring standards.
Scores on the free-response questions are weighted and combined with the results of the computer-scored
multiple-choice questions, and this raw score is converted into a composite AP score of 5, 4, 3, 2, or 1.
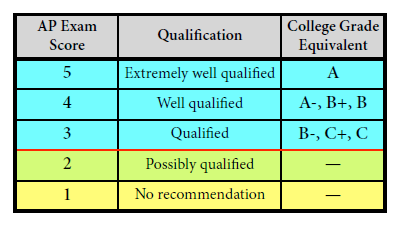
In general, an AP Exam score of 5 is equivalent to the average score among college students earning grades of A in the college course. Similarly, AP Exam scores of 4 are equivalent to college grades of A−, B+, and B.
AP Exam scores of 3 are equivalent to college grades of B−, C+, and C.
and consistency. In each subject, a highly respected college faculty member fills the role of Chief Reader,
who, with the help of AP Readers in leadership positions, maintains the accuracy of the scoring standards.
Scores on the free-response questions are weighted and combined with the results of the computer-scored
multiple-choice questions, and this raw score is converted into a composite AP score of 5, 4, 3, 2, or 1.
In general, an AP Exam score of 5 is equivalent to the average score among college students earning grades of A in the college course. Similarly, AP Exam scores of 4 are equivalent to college grades of A−, B+, and B.
AP Exam scores of 3 are equivalent to college grades of B−, C+, and C.
Using and interpreting AP ScoresThe extensive work done by college faculty and AP
teachers in the development of the course and the exam and throughout the scoring process ensures that AP Exam scores accurately represent students’ achievement in the equivalent college course. While colleges and universities are responsible for setting their own credit and placement policies, AP scores signify how qualified students are to receive college credit or placement. |