About the AP Physics Course
|
Students explore principles of Newtonian mechanics (including rotational motion); work, energy, and power; mechanical waves and sound; and introductory, simple
circuits.The course is based on six Big Ideas, which encompass core scientific principles, theories, and processes that cut across traditional boundaries and provide a broad way of thinking about the physical world. The Following are Big Ideas• Objects and systems have properties such as mass and
charge. Systems may have internal structure. • Fields existing in space can be used to explain interactions. • The interactions of an object with other objects can be described by forces. • Interactions between systems can result in changes in those systems. • Changes that occur as a result of interactions are constrained by conservation laws. • Waves can transfer energy and momentum from one location to another without the permanent transfer of mass and serve as a mathematical model for the description of other phenomena. |
Lab requirement:This course requires that 25 percent of the instructional time will be spent in hands-on laboratory work, with an emphasis on inquiry- based investigations that provide students with opportunities to apply the science practices.
|
How AP exams Are Scored
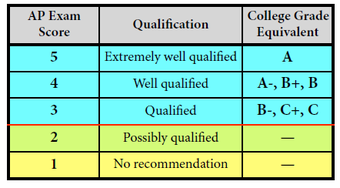
AP Exam Readers are thoroughly trained, and their work is monitored throughout the Reading for fairness and consistency. In each subject, a highly respected college faculty member fills the role of Chief Reader, who, with the help of AP Readers in leadership positions, maintains the accuracy of the scoring standards. Scores on the free-response questions are weighted and combined with the results of the computer-scored multiple-choice questions, and this raw score is converted into a composite AP score of 5, 4, 3, 2, or 1. In general, an AP Exam score of 5 is equivalent to the average score among college students earning grades of A in the college course. Similarly, AP Exam scores of 4 are equivalent to college grades of A−, B+, and B. AP Exam scores of 3 are equivalent to college grades of B−, C+, and C.
Using and interpreting AP
|
Additional resources
Visit apcentral.collegeboard.org
for more information about the AP Program. |
Enrichment ProjectsLinks forthcoming.
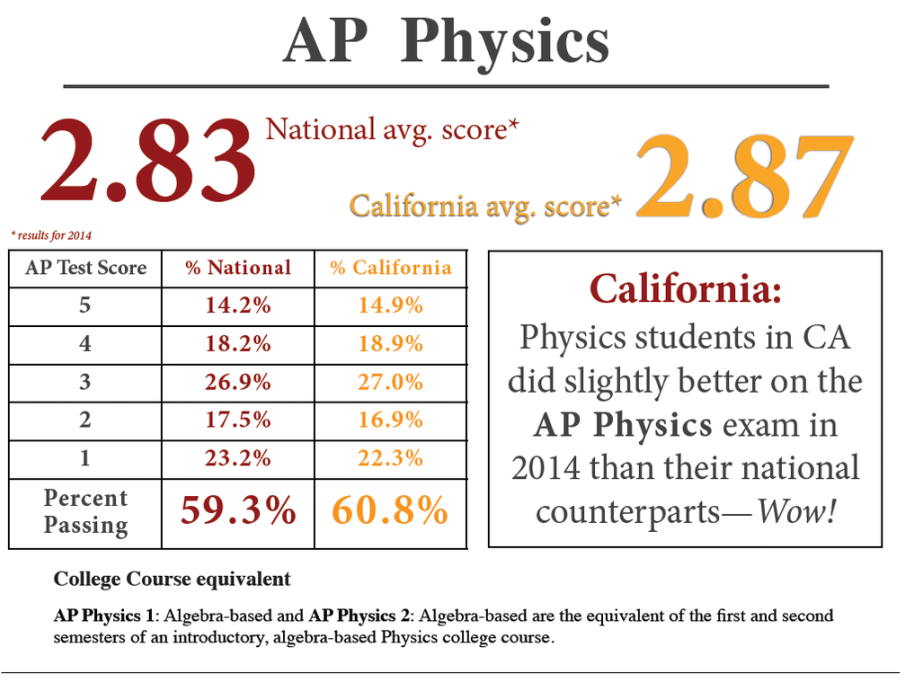
The scores posted on this page are from the old Physics B course. The current Physics 1 course had a national passing rate of 37%, so it is challenging, but doable. Do make sure that all study materials are for Physics 1 and not Physics B/C. Much of the AP test is conceptual problems, so it is more than just chugging through equations.
|